Understanding the Area of a Pyramid: Smart Ways to Maximize Your Calculations in 2025
“`html
Understanding the Area of a Pyramid: Smart Ways to Maximize Your Calculations in 2025
The Basics of Pyramid Area Calculation
The area of a pyramid, a critical concept in geometry, involves understanding both the **base area of a pyramid** and how to combine it with the lateral surfaces. To effectively calculate pyramid area, it’s essential to familiarize yourself with the **area of a pyramid formula**. Typically, this involves determining the base area and adding the lateral area, which requires knowledge of the **slant height of a pyramid**. For example, recognizing that different types of pyramids, like square and triangular pyramids, will influence how you derive these values is crucial. Additionally, understanding how to find the area of a pyramid lays the foundation for more complex geometry concepts, such as calculating volume or surface area, and has real-life applications in architecture and design.
Understanding the Types of Pyramids
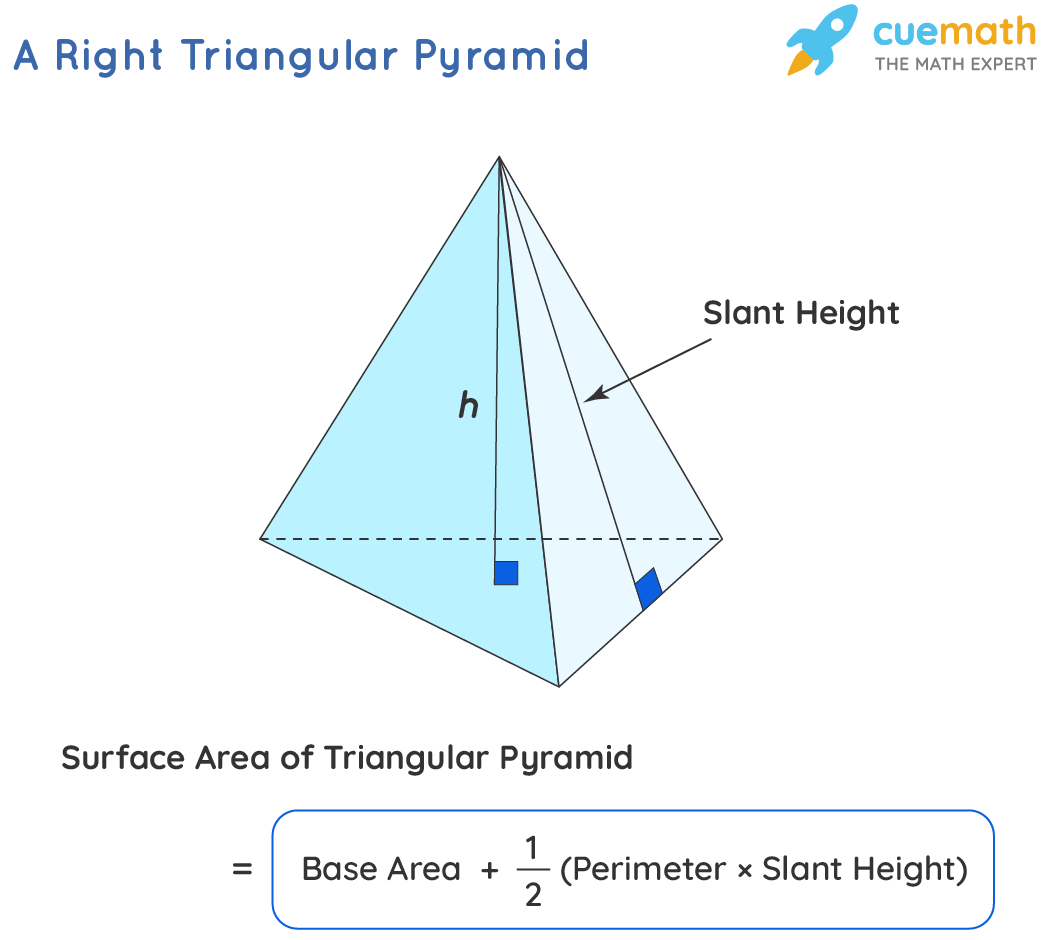
Pyramids come in various shapes and sizes, each defined by their base geometry. For instance, **triangular pyramids** have three triangular faces, while **square pyramids** have a square base. The way you approach calculating the area will depend largely on these types. For triangular pyramids, calculating base area involves using the triangle’s height and base length. Conversely, for square pyramids, the formulas for pyramid area require a simple multiplication of the length of one side squared for base area. This diversity in design leads to various applications of pyramid area in fields such as construction and education, making it a fascinating subject to delve into.
Key Formulas for Finding Area
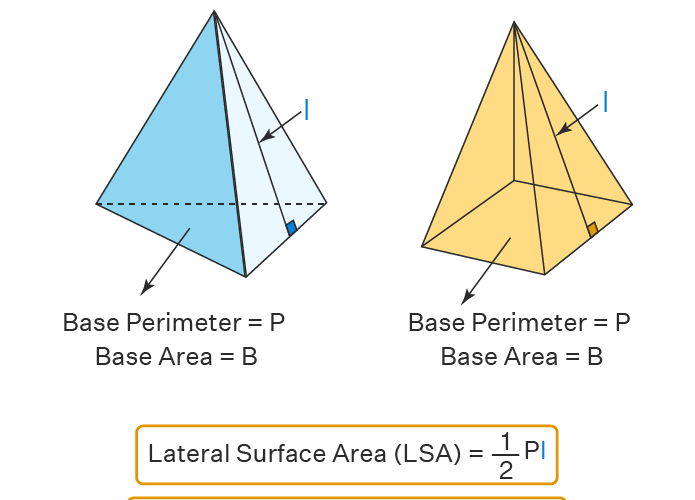
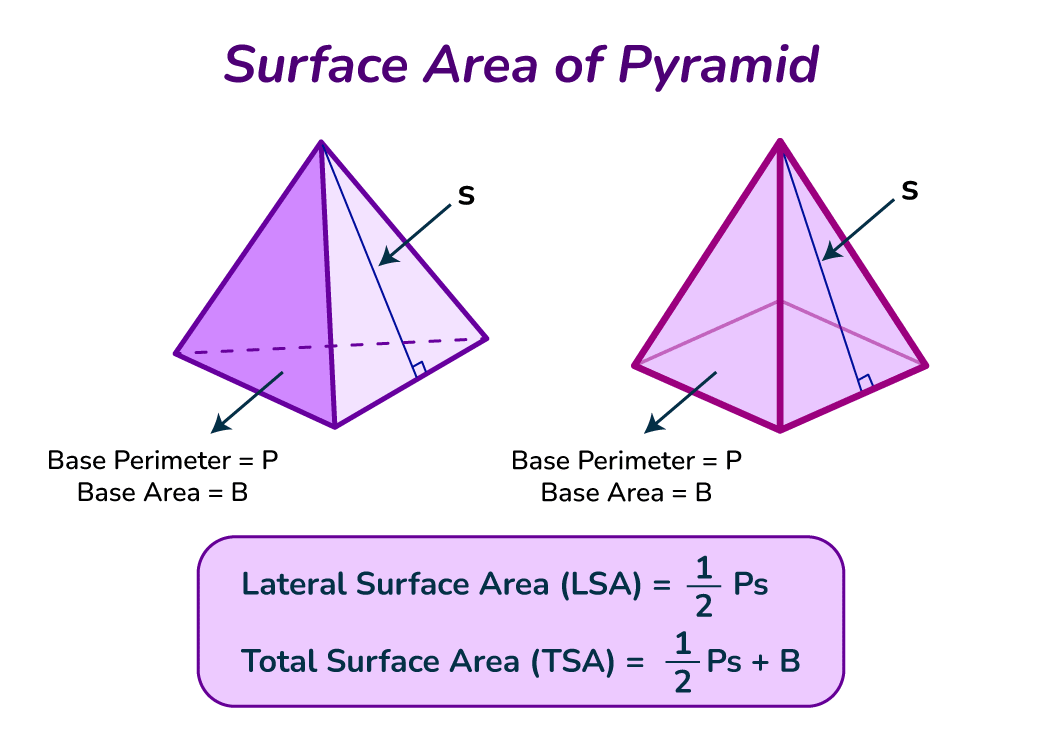
When it comes to calculating the **surface area of a pyramid**, various formulas are pivotal. The total surface area of a pyramid can be computed using the base area and the lateral surface area combined. Specifically, for a square pyramid, the formula reads as follows: A = B + (1/2 * P * l), where B represents the base area, P the perimeter of the base, and l the slant height. Understanding these measurements is critical not just abstractly but also in practical scenarios — such as determining material needed for construction of architectural pyramids or for academic explorations in geometry. Always remember to apply the correct formula based on the pyramid’s shape to ensure accurate calculations.
Maximizing Efficient Calculations
One effective strategy to maximize your calculations when dealing with formulas for pyramid area is to draw or model the pyramid digitally. Using **computerized geometric analysis** can also greatly simplify the understanding of spatial relationships within pyramids. Moreover, practice with examples of pyramid structures—like the famous **Classic pyramids** of Egypt—can illustrate historical applications while strengthening understanding of current geometrical principles. Anticipating how different factors—like a pyramid’s height or shape—alter area calculations can help enhance both intuitive and analytic geometric skills.
Applications of Pyramid Area in Real Life
The application of **pyramid area calculations** extends beyond pure mathematics; it plays a vital role in practical fields such as architecture, construction, and engineering. Developing structural integrity through an understanding of how to calculate **pyramid volume** and area ensures safety and aesthetic value in buildings. Architectural studies often incorporate solutions related to pyramid geometry, exploring both theoretical and real-world uses. Modeling practice in geometry via professional tools can bring these concepts to life and institutionalize their relevance within real-world constraints.
Pyramids in Architecture
Pyramids are utilized extensively in architecture due to their stability and aesthetic appeal. The study of **pyramid designs** incorporates both structural and aesthetic principles, ensuring that edifices are visually compelling while serving functional purposes. One excellent example is the use of pyramidal shapes in roofing to effectively displace snow and rain. Understanding the capacity for area applications not only aids in **calculating pyramid area** but also enhances a designer’s ability to create innovative, spatial responses to environmental challenges, thereby solidifying the importance of mathematical geometry in modern architecture.
Real-World Examples of Pyramid Calculations
In practice, understanding the **calculating height of a pyramid** can be vital during significant construction projects. A case study can illustrate how engineers use **area calculations in engineering**; for instance, they might assess load and stability parameters for a new building designed with pyramid-inspired features. Whether for public infrastructure or educational models, outreach could significantly enhance math instructional practices that utilize tangible pyramid structures in projects. Such educational resources provide practical insights into measuring geometric figures effectively.
Exploring Historical Pyramids
The examination of **historical pyramids**, such as the Great Pyramid of Giza, demonstrates the lasting impact of these geometric shapes. By evaluating these iconic structures, scholars investigate historical and mathematical significance through area calculations and structural designs. The dimensional intricacies involved in ensuring durability have fascinated historians and mathematicians alike, spotlighting the interplay between area and volume as critical considerations from ancient times to today’s developments in architectural geometry. This ongoing exploration highlights categories of **pyramid studies** and education, encouraging appreciation of geometric relationships.
Understanding Pyramid Geometry
Engaging with **pyramid geometry** offers profound insights into three-dimensional shapes and their properties. Grasping the principles of their designs hinges on understanding both basic and complex relationships between dimensions. For example, the relationship between the **slant height of a pyramid**, the height, and the base length requires profound knowledge of geometric reasoning and spatial visualization. Utilizing mathematical theories to rationalize area relationships helps solidify foundational principles, thus enhancing not only academic pursuits in geometry but also everyday practical applications.
Techniques for Teaching Geometry
In teaching geometry effectively, utilizing hands-on activities significantly nurtures geometric understanding. Collaborative pyramid projects in educational settings engage learners in math concepts while providing visual and spatial representations through models. Transforming complex area calculations into more interactive experiences promotes intuitive learning and academic interest in geometry. Employing methods like geometric modeling aids in visualizing how shape and area connect, thus ensuring comprehensive learning outcomes for students. These approaches encourage the development of fundamental math skills that are essential beyond academic life.
Optimizing Area Calculations
When it comes to executing pyramid area calculations efficiently, a systematic technique can greatly assist. Begin with measuring the **dimensions of a pyramid** for precision, as incorrect measurements can skew results significantly. Leverage mathematical modeling and computational methods to explore area optimization techniques. Engaging in interactive geometry experiences can solidify understanding and assist with visualizing geometric shapes. Utilizing digital tools for geometric complexities also prepares students and professionals alike for future advancements in **architectural geometry**.
Visualizing Pyramid Models
Visualizing pyramid models extends beyond static structures into dynamics, enhancing spatial reasoning capabilities. Such modeling can be integrated into educational platforms to offer an enriching experience, promoting engagement through geometrical constructs. Comparing different pyramid shapes and areas can elicit discussions on mathematical proofs or basic area measurement techniques. Investing in structural integrity through proper pyramid analysis—focused on **external area** and volume—leads to accurate design in real-world applications, making every calculation count.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding the area of a pyramid is critical for academic and practical applications.
- Different types of pyramids require varied calculation methods, from triangular to square models.
- Real-world applications of pyramid area in architecture highlight the significance of solid geometry.
- Effective teaching methodologies enhance comprehension and student engagement in geometric concepts.
- Proper modeling can facilitate better understanding and optimization of area calculations.
FAQ
1. How do you calculate the surface area of different types of pyramids?
The surface area of any pyramid can be calculated using specific formulas based on its shape. For instance, for a square pyramid, the formula is A = base area + lateral area = B + (1/2 × perimeter × slant height). For triangular pyramids, the approach remains similar but focuses on the triangular base to ascertain the base area, totaling up all surface points.
2. Why is understanding the slant height of a pyramid important?
The **slant height of a pyramid** is crucial for determining the lateral area of the pyramid and plays a significant role in calculating the surface area effectively. It connects the apex of the pyramid to the midpoint of the base edge, influencing how the structure performs under various stress conditions, thus resonating with architectural integrity and stability.
3. What are some real-world uses of pyramids beyond simple geometry?
Pyramids serve as effective designs in architectural and engineering projects, including iconic buildings and monumental structures. They provide stability to sports arenas, roofs, and educational spaces while representing a significant choice for memorials and artistic constructions capable of drawing public interest through both aesthetics and functionality.
4. How can one teach pyramid area calculations to students?
Teaching pyramid area calculations can be engaging through interactive projects and hands-on activities. Encourage students to model pyramids using everyday materials, enabling them to derive formulas based on their experiences while developing a solid understanding of geometric properties in real-time.
5. Where can I find more comprehensive resources on pyramid geometry?
Comprehensive resources can be found in educational websites, geometry textbooks, and specialized architecture literature. Online platforms often offer detailed courses featuring interactive tools and engaging activities to provide deeper insights into aspects of **pyramid geometry** and its real-life implications.
6. Why should we explore different types of pyramids in our studies?
Exploring different types of pyramids expands understanding of geometric concepts, enhances problem-solving skills and fosters appreciation for diverse applications within culture, nature, and human architecture. Recognizing the similarities and differences in pyramid shapes encourages broader learning in both theoretical and practical contexts.
7. How does the volume of pyramids differ from their area?
The volume of a pyramid, calculated using the formula V = (1/3) × base area × height, emphasizes the spatial capacity within the pyramid, while area calculations focus solely on surface measurements. This distinction underscores the necessity for comprehensive approaches in studying pyramids, playing into numerous real-life applications and designs.
“`